
NERC CIP Standards: How to Protect Your Bulk Electric System from Cyber Threats
The reliable supply of electricity is crucial for the smooth functioning of modern society. But this crucial infrastructure is in danger of cyber threats. This kind of threat can disrupt power grids. It can cause widespread outages and interrupt essential services.
Keeping the power grid cyber-secure is pivotal for maintaining the reliability of power supply. This highlights the North American Electric Reliability Corporation Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) standards. NERC plays a crucial role in addressing this challenge. Let’s explore how!
The Imperative Role of NERC in Ensuring Grid Reliability and Security
NERC CIP standards regulate and enforce Bulk Electric System (BES) security in North America. They concentrate on cybersecurity measures. The main goal is to ensure a reliable and efficient supply of electricity across North America's BES.
NERC evolved from a voluntary organization formed in the aftermath of the 1965 Northeast blackout. This pivotal entity handles the reliability and security of the interconnected power systems. Its mission is to reduce risks to the reliability and security of the grid. NERC oversees the BES in the United States, Canada, and part of Baja California, Mexico.
Some key aspects that highlight NEC's role:
- NERC has the authority to enforce mandatory reliability standards. It includes imposing penalties for non-compliance which makes it a powerful entity.
- It oversees more than 1,900 owners, operators, and users of the bulk power system. This is to ensure reliable operation of these NERC registered entities.
- NERC monitors the bulk power system, looking for reliability risks. It can issue alerts and warnings when it detects threats.
- It conducts periodic assessments to identify reliability issues and vulnerabilities in the system.
- NERC also investigates major grid disturbances. This strategy can gather patterns to prevent recurrences. For example, it investigated the 2011 Arizona-Southern California outages.
We now understand the role of NERC in safeguarding North America's power grid. It's also essential to delve into the specific components of these important standards.
Understanding the Core Components of NERC CIP Standards
NERC CIP standards govern the critical infrastructure of all entities that impact the reliability of BES. This includes owners, operators, and users of any part of the system. These standards are not only guidelines but have the force of regulations, making them binding.
Some key facets of NERC CIP standards:
- They apply to both physical assets like substations, as well as cyber assets like backup control systems.
- The standards categorize BES assets into different impact levels. Mandates need stricter controls for assets with higher impact levels.
- NERC CIP standards encompass different areas. These areas include security management, personnel training, access control, and recovery plans.
- Compliance is mandatory and enforced through fines, sanctions, and other penalties. Self-reporting violations can reduce penalties.
They update the standards to address emerging cyber threats and adapt to new technology. Additionally, they incorporate lessons learned from past experiences.
You now know the NERC CIP standards' core components. This is crucial in recognizing their role in cybersecurity. After all, in today's digital age, the threats are not only physical but virtual.
The Role of Cybersecurity in NERC CIP Standards
Utility companies in North America must establish and follow essential cybersecurity measures. The goal is to ensure that strong security controls are in place to shield the BES and its users from threats. In this way, they could reach their optimal functioning. Such threats encompass cyber- attacks, cyber vandalism, and acts of cyber terrorism.
Some key cybersecurity aspects of the standards:
- Mandating strong access controls like multi-factor authentication for critical assets.
- Requirements for continuous vulnerability monitoring and risk assessments.
- Incident response procedures and reporting timelines.
- Encryption of data-in-transit and data-at-rest.
- Stringent physical security controls for cyber assets like surveillance and alarms.
- Contingency planning through disaster recovery procedures and backups.
NERC aims to create a resilient Bulk Electric System. They will do it by incorporating these cybersecurity best practices. So that it can have the ability to ward off and recover from cyber intrusions.
The standards provide a robust framework for cybersecurity. But it's vital to ensure adherence to these guidelines. This brings us to the mechanisms in place to track and enforce compliance.
Compliance and Enforcement of NERC CIP Standards
Did you know that NERC CIP violation cases are increasing year-on-year? In 2017 alone, it registered 190 cases? There are various reasons for such critical violations. We listed some of these causes and their occurrence percentage below.
Causes of NERC CIP Violations
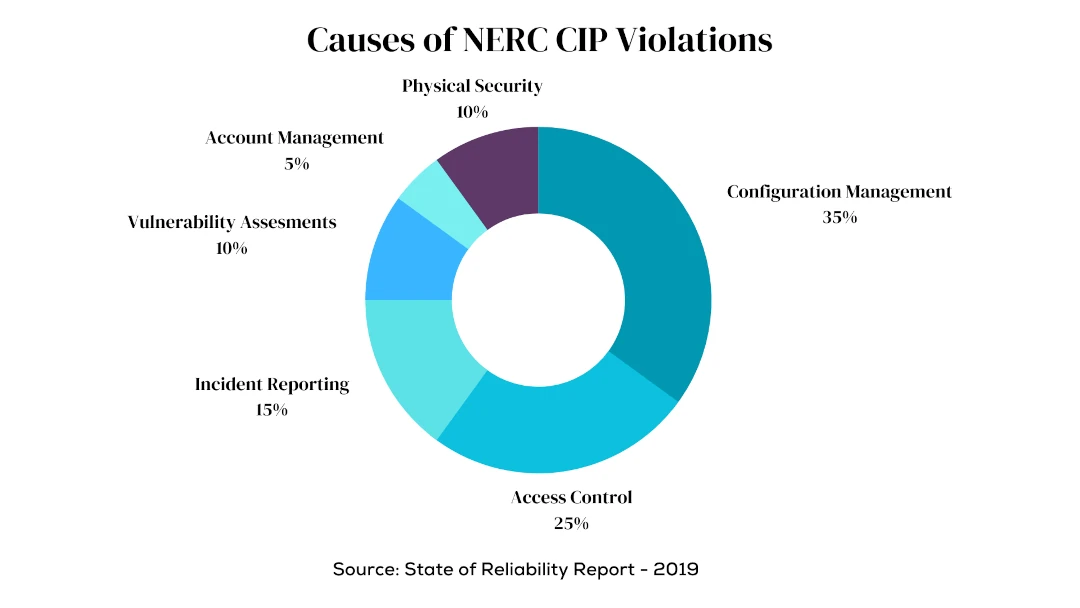
Source: 2019 State of Reliability Report
- Cause: Configuration Management
Percentage: 35% - Cause: Access Control
Percentage: 25% - Cause: Incident Reporting
Percentage: 15% - Cause: Vulnerability Assessments
Percentage: 10% - Cause: Account Management
Percentage: 5% - Cause: Physical Security
Percentage: 10%
NERC's Compliance Monitoring ensures uniform compliance among covered entities. They achieve this through conducting regular audits and spot checks. Non-compliance with NERC CIP standards can lead to monetary fines, sanctions, or other punitive actions. The penalties can vary since NERC operates across many countries.
With enforcement in place, NERC CIP standards go beyond guidelines. It is more of a commitment to safeguard North America's power grid and provide the best service.
Case Study: Responding to High Power Demand during Cold Weather
In January 2018, a prolonged period of extreme cold weather caused a spike in electricity demand across the Midwest United States. This event stressed the region's electrical grids. The peak demand was more than 140,000 MW, leading to power shortages and rolling blackouts.
In response, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) and NERC conducted an investigation. The investigation focused on grid operations, communications, and coordination between entities. It also explored steps to enhance future winter readiness.
Several recommendations emerged from the investigation:
- Increase coordination between gas and electric system operators during severe weather events.
- Review emergency operation plans before the winter season.
- Ensure adequate fuel supplies and advance procurement of natural gas.
- Improve load forecasting methodologies by factoring in extreme weather scenarios.
This immediate action of NERC has proven its effectiveness in safeguarding the grid. The collaborative investigation with FERC also highlighted NERC's coordination with regulatory authorities.
Here are some of the questions often asked to provide more understanding of the role of NERC.
FAQs in NERC’s Cybersecurity Standards
1. How does NERC ensure that its cybersecurity measures are up-to-date?
NERC always reviews and updates its CIP standards. It gathers inputs from industry experts, regulators, and security researchers. It also has dedicated cybersecurity teams that watch emerging threats. Also, NERC's cybersecurity wing, the Electricity Information Sharing and Analysis Center (E-ISAC) helps. It is developing new security programs.
2. What are the consequences for entities that fail to follow NERC's mandatory reliability standards?
Noncompliance can result in sanctions and financial penalties by NERC and regulatory authorities. In extreme cases of negligence, entities may also face stricter oversight. They can receive suspension orders, or revoke of operational certification. The penalties aim to deter lax security practices.
3. How does NERC collaborate with international entities?
NERC coordinates with Canadian authorities through formal agreements. It also partners with the European Union Agency for the Cooperation of Energy Regulators. They collaborate with international groups to share best practices.
Final Thoughts
In summary, the NERC CIP standards serve as the first line of defense. They secure the North American bulk electric system and fight against cyber threats. This is to ensure to never disrupt the essential services. As cyber- attacks become rampant, it is more crucial to put a safety measure in place. And the role of NERC CIP is crucial in bolstering our critical infrastructure's cybersecurity defenses.
Loading comments...


